One of my favourite scenes from the ‘3 Idiots’ movie is when Rancho is asked about the definition of ‘Machine’ by his Professor. We all know and love Rancho’s simplified version of the ‘3 idiots’ machine definition, but the professor didn’t seem to appreciate it. Instead, he was much more impressed by Chatur’s definition, which many of us, if not all, skipped over. In this blog, I will simplify the 3 Idiots machine definition for you.

- 3 idiots machine Definition:
- 1st part – "Machines are any combination of bodies so connected that their relative motions are constrained."
- 2nd part – "and by which means, force and motion may be transmitted."
- 3rd part – "as a screw and its nut, or a lever arranged to turn about a fulcrum or a pulley about its pivot, etc."
- 4th part – "especially, a construction, more or less complex, consisting of a combination of moving parts, or simple mechanical elements, such as wheels, levers, cams, etc."
Of course, it’s not a great idea to mug up things without understanding (we have already discussed this point in Understanding Projectile Motion), but the definition of a machine that he gives is also quite impressive. It goes something like this:
If you are interested, you can watch 3 idiots on Amazon Prime by clicking HERE
3 idiots machine Definition:
“Machines are any combination of bodies so connected that their relative motions are constrained and by which means, force and motion may be transmitted and modified as a screw and its nut, or a lever arranged to turn about a fulcrum or a pulley about its pivot, etc. especially, a construction, more or less complex consisting of a combination of moving parts, or simple mechanical elements as wheels, levers, cams etc.”
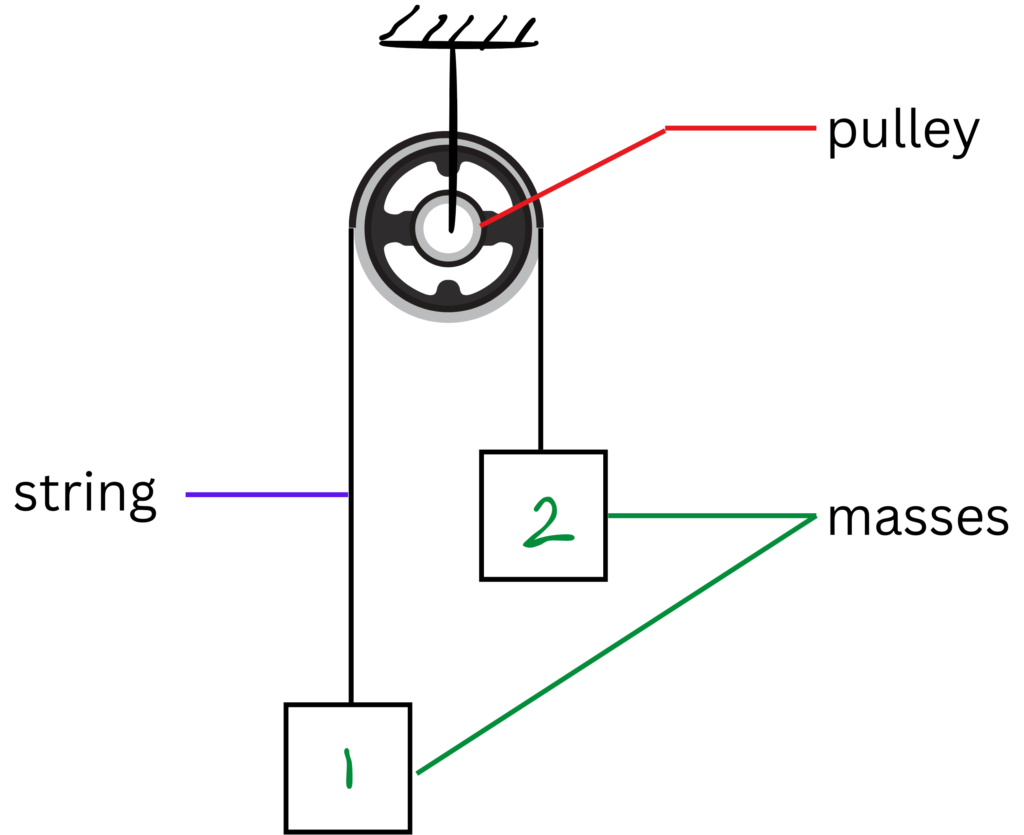
In today’s blog, we will be breaking this definition down with the help of a very simple example, which most of us (from PCM or PCB background) have studied, i.e., the Atwood machine – the simplest pulley-block system.
Let’s divide the 3 idiots machine definition into parts and try to get this thing sorted out quickly :
1st part – “Machines are any combination of bodies so connected that their relative motions are constrained.“
Look at bodies 1 and 2. Both the masses are so connected that their motions are dependent on one another. That’s what we call – ‘the relative motion is constrained.’
We can write the constraint relation for the displacement between the two masses for this case as :
*Refer to this article for a detailed discussion on writing constrained relations: Click Here
It shows that if 1 comes down by ‘x’ metres, then 2 has to move up by ‘x’ metres. It’s all constrained!

2nd part – “and by which means, force and motion may be transmitted.“
The gravitational force on 1 (m1*g) is transmitted through the string to affect the motion of 2.
Also, if 1 and 2 are of the same mass, they don’t have any acceleration, but in case the masses are different, the accelerations of 1 and 2 get modified.
We write the FBD (free body diagram) equation for each body as :


3rd part – “as a screw and its nut, or a lever arranged to turn about a fulcrum or a pulley about its pivot, etc.“
This part explains various examples of simple machines (screw-nut, lever, pulley).
Here, in these examples, we have a pulley as a simple machine component as a part of this whole system.

4th part – “especially, a construction, more or less complex, consisting of a combination of moving parts, or simple mechanical elements, such as wheels, levers, cams, etc.“
Compared to a simple machine like a pulley, we can say that the Atwood machine system arrangement would come under a complex combination that has many moving parts in it, such as :
- Masses
- String
- Pulley
This was a short and fun kind of post explaining the famous 3 idiots machine definition, just to make sure that all of the 3 idiots movie lovers can now break down this definition the next time they watch the movie! My aim was to explain this thing in the simplest way possible.
Also, I would like to add that just memorizing blindly doesn’t make any sense, but understanding the definition would really help us to make our grip on the concepts much better. I would also be quite impressed if Chatur had the understanding of this beautiful definition. But sadly, the character ‘Chatur’ doesn’t seem to be interested in all this 🙁
Keep Learning!















